HAL WiFi Introduction
The SLN-VIZN3D-IOT board is equipped with an Azurewave Technologies AW-AM510 WiFi Module, which supports 802.11a/b/g/n on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, as well as supporting Bluetooth 5.1.
For the time being, the requirements for the WiFi cover:
- Module hardware initialization
- Local access point connection
- Connect to a non-secure FTP server with anonymous credentials
Integrating the WiFi module
The WiFi module is a special type of peripheral which acts as both an input and an output. Despite this fact, integrating the WiFi module with the framework can be done by registering both an input device, and an output device.
caution
Because the module is registered to two managers at the same time, some degree of synchronization needs to be implemented to avoid various race conditions.
WiFi Task
The WiFi initialization task will automatically create several other tasks to handle TCP Connections, module communication, and the WiFi dispatcher. However, because WiFi operations are slow compared to the speed at which the CPU operates, the calling task will block waiting for an answer.1
info
1 To alleviate this issue, the NXP driver supports asynchronous operation, however the code complexity will grow and the need for synchronization will increase.
In order to avoid blocking important resources like the Output Manager task or the Input Manager task, the WiFi device must maintain a standalone execution task in which waiting operations can be performed with minimal impact to the rest of the system.
The communication between the WiFi, Input Manager, and Output Manager tasks uses an event-driven design which can help to decrease the number of potential errors caused by race conditions.
The following diagram presents the components involved.
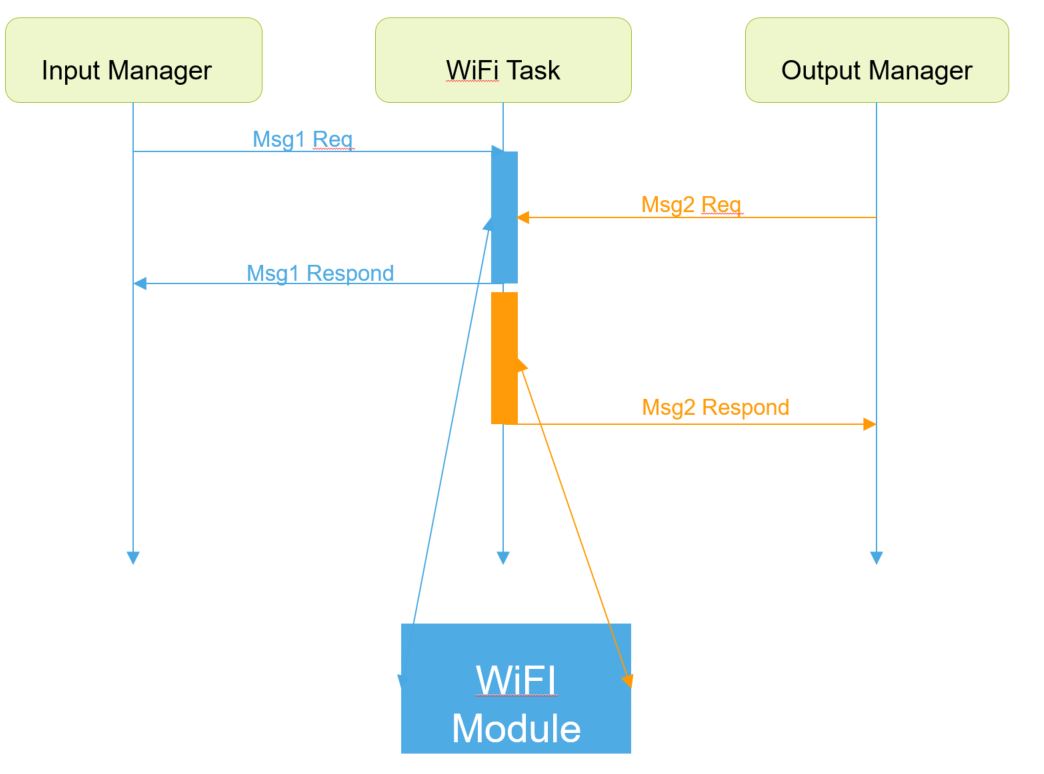
The function logic in order to connect to an access point is as follows:
BOARD_InitWIFIAW_AM510Resource()- Initialize hardware pinsWPL_Init()- Load the WiFi firmware on the AW-AM510 chipWiFi_GetCredentials (&credentials)- Get the saved credentialsWPL_Join (credentials)- Join the network specified by the credentials.
FTP Client
The Smart Lock application is capable of maintaining brief videos which have been captured by the camera. This feature can be useful in applications where a user wants to review important activity captured by the camera.
After encoding a captured image frame,
the Output Manager will send a message to the WiFi Task via the InferenceComplete callback
which contains a pointer to the location and the size of the video.
After that,
the WiFi task will kick off the procedure to establish a connection with an FTP server.
Connecting to an FTP server uses a handshake procedure similar to the process of connecting to an access point. The steps are as follows:
FTP_InitFTP_ConnectBlockingFTP_StoreBlockingFTP_DisconnectBlocking
FTP_Init();
ftp_session_handle_t handle = FTP_ConnectBlocking();
if (handle != NULL)
{
FTP_StoreBlocking(handle, remote_path, recordedDataAddress, recordedDataSize);
FTP_DisconnectBlocking(handle);
}
/**
* @brief Fetches the Server Info from the flash, init internal structures.
*
* @return kStatus_Success on success
*/
status_t FTP_Init(void);
/**
* @brief Connect to the server specified by saved server_info
*
* @return Return a handler which is to be used with the store/disconnect function. NULL if no connection was done
*/
ftp_session_handle_t FTP_ConnectBlocking(void);
note
For now only anonymous unsecured FTP connections are supported.
In order to supply credentials for the FTP server,
modify the FTP_ConnectBlocking function in ftp_client.c.
ftpSession.user = "anonymous" /* set manually the user */;
ftpSession.pass = "anonymous@domain.com" /* set manually the password */;
After changing the code, rebuild and reflash the application.
/**
* @brief Store the data at a specific remote location.
*
* @param sessionHandler Session handler obtain after the connect operation took place
* @param remote_path Remote path at which to save the file. Should contain the name of the file
* @param data_source Data to be saved
* @param len Length of the file
* @return kStatus_Success on success. If the status was fail, automatic disconnection takes place
*/
status_t FTP_StoreBlocking(ftp_session_handle_t sessionHandler, const char *remotePath, char *dataSource, uint32_t len);
/**
* @brief Disconnect from a connected server
*
* @param sessionHandler
* @return kStatus_Success on success
*/
status_t FTP_DisconnectBlocking(ftp_session_handle_t sessionHandler);